Numerous things can be done to secure remote access, including setting up a strong password, timely upgrading the software, setting up two-factor authentication, and more.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Use a strong password and two-factor authentication to prevent hackers from accessing the system.
- Make sure that the network is always secured with a VPN.
- Employees should be educated on emerging threats in a remote setting.
- All devices should be protected with a firewall and antivirus software.
- Keep all the remote access software updated.
Remote work has become a trend in this digital era. Now employees can work from their comfort and still be able to give maximum productivity. There are even specialized remote work software now, and its market was estimated at $23.2 billion in 2023.
However, remote work is also exposed to several vulnerabilities, like data breaches. This can mess up the whole operations and businesses can sustain major losses. So, is there any solution?
Well, in this article, I’ll mention how to prevent remote access vulnerabilities and strengthen network security.
Ever since COVID-19, companies and firms have started shifting towards remote work. In this, team members, workers, etc., can do their work from any place. There are no geo-restrictions, and the productivity remains the same.
However, while this is convenient, new risks have also emerged. For example, when the connection is not secured, hackers can break in and get their hands on sensitive information. There are vulnerabilities as well, like outdated software, weak login credentials, or unsecured devices.
Until and unless someone has proper knowledge of what threats are, they won’t be able to come up with proper solutions. But if they do understand the risks completely, they can create a safe and secure environment.
Common remote access vulnerabilities include things that you might think are not a big deal. For starters, setting up a weak or easy-to-guess password is not a smart move; hackers can easily guess it and get access.
While working remotely, remote access tools are used, and they need to be always updated because this way latest security features are automatically in play. But if they are outdated, buckle up because you just exposed them to various vulnerabilities.
Malware and phishing attacks are common, and anyone can click on unknown links or get scammed, so be aware. These are just some of the common issues that people often ignore until it’s too late.
Here are some key strategies to prevent remote access vulnerabilities:
Two-factor authentication acts as a layer of security that prevents entry to systems with a password alone. It combines what you know (say, a password) with something you have (like a phone or key) or something that is uniquely yours (your fingerprint).
This makes it difficult for hackers to log in, even if they have stolen your login information. Two-step verification is one of the simplest and most powerful measures you can take to lock down your remote access points.
Security holes are often repaired through such software updates. Remote access business tools and the operating systems they run on that are not up-to-date are vulnerable to attack by cybercriminals. Having the most up-to-date version means known vulnerabilities are not left exposed to attackers until they are patched.
Remote connections are encrypted so that the data passing between the user and the network can to be intercepted by hackers. Combine VPNs with powerful encryption algorithms that add a strong layer or two of security.
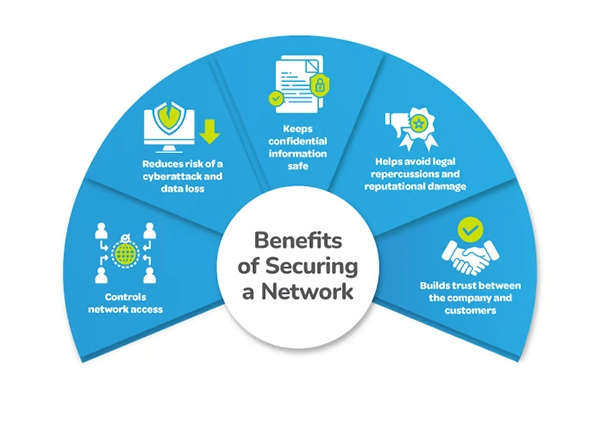
Stay away from free or public VPNs as they make it hard to protect you. A safe connection is important for both user data and company assets. Below, you can see the key benefits of securing a network.
Many remote workers connect to corporate infrastructure with their personal or mobile devices. These end points need to be protected with firewalls, antivirus, and device encryption.
Firm policies regarding device usage should be enforced, and all endpoints should comply with security requirements. It helps to stop malware infections or unauthorized devices from gaining access, should one be.
Zero Trust upends the notion that devices and users can be trusted, even if they’re inside the network. Each access request is authenticated with identity, device, and contextual information before it is permitted.
Zero Trust execution diminishes the likelihood of internal/ lateral threats that have the potential to spread through the network.
DID YOU KNOW?The global firewall service had a market size of $3.85 billion in 2024!
Employees are often the biggest risk in an organization’s cybersecurity. Regular training on password hygiene, phishing awareness, safe browsing, and the risks of using insecure networks is critical. Remote workers are a particularly soft target and need to be educated about what to look for and how to report it.
Training on cybersecurity should be continuous to enable employees to be abreast of the changing threats and best practices. Employees who are educated about security are more apt to adhere to corporate policies and make sound security decisions.
It’s important to educate your employees about security and the steps they need to take and the things they need to avoid. Make sure to conduct programs consisting of the importance of strong passwords, phishing attacks, and safe browsing habits to avoid any security breach.
While it is significant for office workers, it is even more crucial for remote employees. They are exposed to security risks and have to take steps carefully to avoid getting in trouble. It doesn’t take time to learn all this, so just 1-2 sessions are going to be enough.
Always choose the best remote access solutions. This includes safe VPN’s, virtual desktops, and endpoint management systems. There are several platforms available, so make sure to compare them and go for the one that meets all your needs and requirements.
Remote access vulnerabilities are quite common, and usually, employees are the weakest link. It’s important to implement good network protection and educate your employees so they don’t make any mistakes.
Remote access is helpful and is typically considered a comfort, where productivity is maintained. So, make sure to get the best network protection like strong VPN’s and a management system.
Numerous things can be done to secure remote access, including setting up a strong password, timely upgrading the software, setting up two-factor authentication, and more.
To secure your network connection at a remote site, make sure to have a good antivirus installed along with a firewall and apply data encryption.
Remote access protection refers to security measures that ensure only authorized users and devices can access internal systems from outside the organization’s network.
