High-quality hardware from reliable sources often comes with built-in security features and adheres to the latest standards, making the network more secure from the start and reducing the need for additional security measures.
In an increasingly interconnected world, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a foundational element of modern life, but its rapid expansion has also created new security challenges. The LoRaWAN protocol, designed for low-power, wide-area networks, is a crucial part of this ecosystem, connecting countless devices over long distances.
However, this convenience is also associated with an increased risk of security breaches. According to Verizon’s 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report, one in three data breaches now involves an IoT device.
This statistic highlights the urgent need for robust security protocols to ensure the integrity and reliability of LoRaWAN gateways. The following information provides a guide to the key security measures that are essential for safeguarding your network.
Let’s understand the essential security protocols here!
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Choosing high-quality gateways and sensors provides an essential foundation for network security.
- LoRaWAN networks use AppKeys to ensure that only authorized devices can connect to the gateway. This mutual authentication process prevents unauthorized access.
- Data transmitted is encrypted and scrambled using algorithms, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- A special network key is also used to detect any unauthorized changes to the data.
- To prevent cyberattacks that resend old messages to confuse the network, LoRaWAN gateways use a frame counter.
- If a message’s frame counter does not match the system’s logs, it is ignored, preventing unauthorized data from being re-sent.

The best thing you can do for setting up a dependable LoRaWAN gateway operation is to pick up the best hardware that you can find. Not all gateways and sensors are the same. Superior gateways boost your connection’s dependability and offer extra security features.
Choosing the best hardware for a LoRaWAN network purchase is nearly as important as what you purchase. You want to source your hardware from a business that shows leading LoRaWAN expertise and has several years of experience in that niche.
Only functional hardware that complies with the most recent network security standards will be sold to you by a trustworthy sourcing partner.
One thing you don’t want to cut corners with is hardware, especially when setting up something as sensitive as a LoRaWAN gateway. When you have to invest more time and money in network security, any savings you may have from purchasing a less expensive gateway will be lost.
Establishment of authentication is one of the key features of LoRaWAN networks. Devices and networks must mutually authorize one another before any device can connect to a gateway. This keeps your device from connecting to unauthorized devices via your LoRaWAN gateway to a malicious network.
An authentication key is the most popular authentication method used by LoRaWAN gateways. Also called AppKeys or AppSKeys, these keys are independently generated and only used for this specific connection.
Authentication keys add an essential layer of security for LoRaWAN gateways. Make sure that this protocol is turned on for all of your gateways to prevent unauthorized access.
INTERESTING FACT
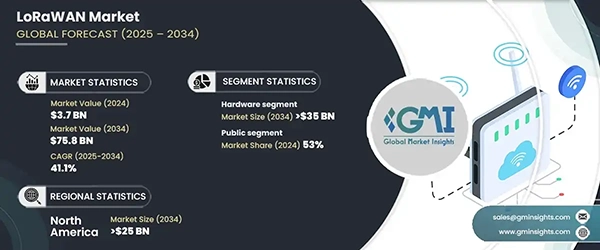
The worldwide LoRaWAN market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41.1% between 2025 and 2034, from its 2024 valuation of USD 3.7 billion.
Here comes to another layer in LoRaWAN security protocols –integrity protection. Data is jumbled by the LoRaWAN gateway using multiple layers of encoding and algorithms, rendering it unintelligible to external parties. Only authorized devices possess the application session key, which is required to access the encrypted data; unauthorized devices are unable to generate this key.
In this process in a LoRaWAN gateway also involve a key for analyzing data on the receiving end. Any changes to the data that were not made using the current security protocol are detected by the receiving device using a unique network key. Knowing if the data has been compromised, support network administrators to diagnose potential security breaches.
Common forms of cyberattacks don’t attempt to generate new data or messages because they recognize that devices are capable of distinguishing data from unfamiliar sources. Instead, they try to resend a message that was prompted by an authorized source within the network and mimic the trusted device. That creates confusion within the network and hides transactions and interactions that were never authorized.
Replay protection is built into LoRaWAN gateways to stop this from occurring in all network-device interactions. Each data connection or transmission has a unique number assigned, called a frame counter.
If the frame counter doesn’t match the system’s logs, it is ignored. That way, if an authorized party resends a message, the system recognizes that there is one additional message than that was sent by the authorized gateway or device and ignores it.
By now somewhat outdated, the view of the Internet of Things as a network that is vulnerable to security breaches. The last few years have seen a significant advancement in network protocols, which has improved security and added layers of protection against possible breaches.
LoRaWAN gateways works as important nodes in the network for connection and security. Many security protocols, including replay and integrity protection against data breaches and authentication keys to stop unwanted access, are built into modern gateways to safeguard the network and the devices connected to it.
You may get the latest hardware for your LoRaWAN gateway, if you care about security. The most recent technology includes built-in security protocols that don’t require you to do anything else to secure your network.
High-quality hardware from reliable sources often comes with built-in security features and adheres to the latest standards, making the network more secure from the start and reducing the need for additional security measures.
An authentication key ensures that both the device and the network can mutually verify each other’s identity before establishing a connection.
During transmission, the receiving device uses a special key to check for any unauthorized alterations, ensuring the data’s integrity.
A replay attack involves a malicious party re-sending an authorized message to the network. LoRaWAN prevents this by assigning a unique frame counter to each data transmission.
